Welcome to our websites!
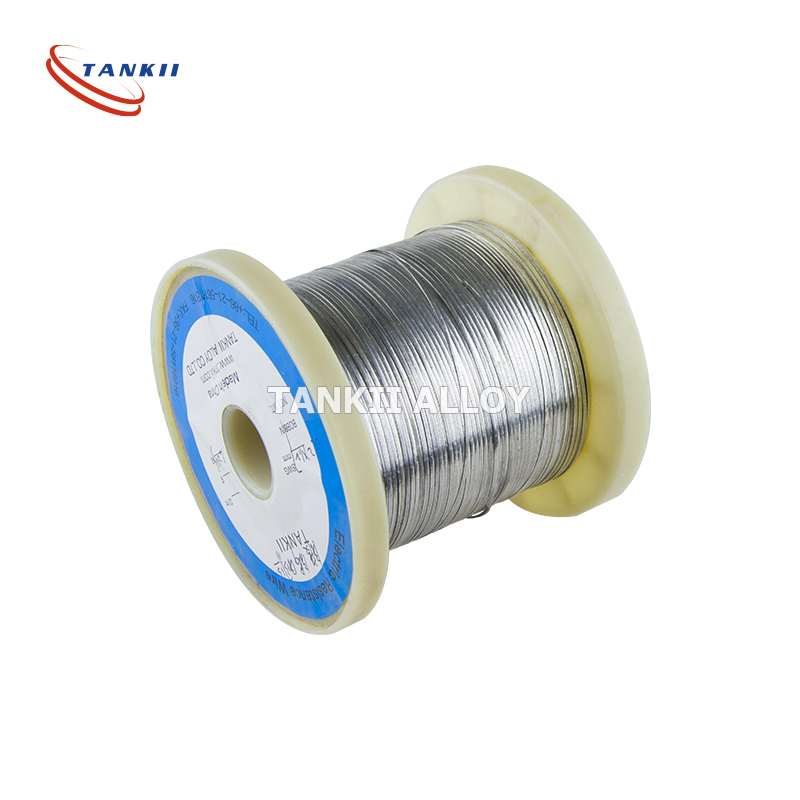
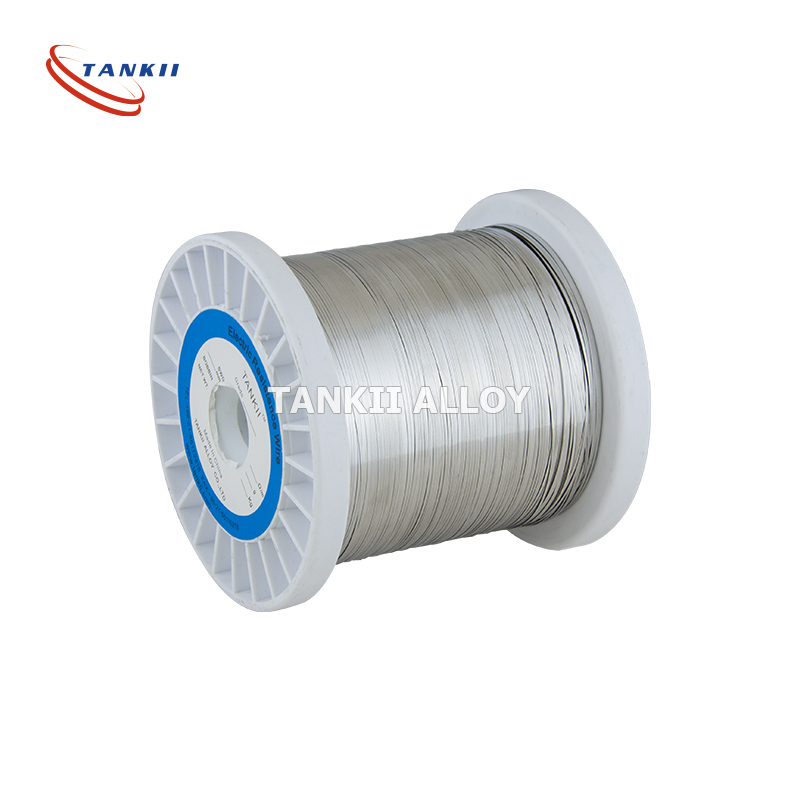
Constantan Alloy Flat Wire 6j40 Nickel Copper Flat Wire
Constantan alloy Flat wire 6j40 Nickel copper flat wire
Constantan Definition
Resistance alloy with moderate resistivity and low temperature coefficent of resistance with a flat resistance/temperature curve over a wider range than the ”manganins”. CuNi44 Alloy wire also shows better corrosion resistance than the man ganins. Uses tend to be restricted to ac circuits. CuNi44/ CuNi40 /CuNi45 Constantan Copper Nickel Alloy Wire is also the negative element of the type J thermocouple with Iron being the positive; type J thermocouples are used in heat treating applications. Also, it is the negative element of the type T thermocouple with OFHC Copper the positive; type T thermocouples are used at cryogenic temperatures.
Chemical Content(%) CuNi44
| Ni | Mn | Fe | Si | Cu | Other | ROHS Directive | |||
| Cd | Pb | Hg | Cr | ||||||
| 44 | 1.50% | 0.5 | - | Bal | - | ND | ND | ND | ND |
Mechanical Properties CuNi44
| Max Continuous Service Temp | 400 ºC |
| Resistivity at 20ºC | 0.49 ± 5% ohm*mm2/m |
| Density | 8.9 g/cm3 |
| Temperature Coefficient of Resistance | < -6 ×10-6/ºC |
| EMF VS Cu (0~100ºC) | -43 μV/ºC |
| Melting Point | 1280 ºC |
| Tensile Strength | Min 420 Mpa |
| Elongation | Min 25% |
| Micrographic Structure | Austenite |
| Magnetic Property | Non. |
Write your message here and send it to us